

- Mac os firewall settings for open wireless networks for mac#
- Mac os firewall settings for open wireless networks windows#
Mac os firewall settings for open wireless networks windows#
Mac os firewall settings for open wireless networks for mac#
In this regard, why would you block all incoming connections to your computer?īlock all incoming connections will prevent legitimate network connection, attempts including all forms of file sharing in OSX, remote access connections with SSH or SFTP & any other similar network service that allows for Mac network connections from trusted logins. The firewall manages this by tracking the state of connections (such a firewall is often called a Stateful Firewall). So if outbound new connections are allowed, then the incoming half of that exchange is okay. Both active and inactive network interfaces are listed, in the order that they are used by the OS and with a lot of details (MAC-address, interface name, router, subnet mask etc.).“ Incoming block” means that incoming new connections are blocked, but established traffic is allowed. Applications/Server.app/Contents/ServerRoot/usr/libexec/afctl -w 10.10.10.2įinally, the script network_info.sh shows information about a Macs network configuration.

View how the Server app interprets your network settings:

Make an alias for looking at what has a listener open, called ports:Īlias ports='lsof -n -i4TCP | grep LISTEN' What binaries have what ports and in what states are those ports: Tcpdump -qns 0 -A -r /var/tmp/capture.pcap Read tcpdump (cap) files and try to make them human readable: Setup a network listener on port 2196 for testing:Ĭapture all the packets for a given port going to a given destination of 10.0.0.48:Ĭapture the packets as above but dump to a pcap file: usr/bin/nc -v -w 15 2195Įstablish a network connection with only allowing ipv4 Scan port 80 of /System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Network\ Utility.app/Contents/Resources/stroke 80 80Įstablish a network connection with nc -v 80Įstablish a network connection with over port 2195 View network information as it happens (requires ntop to be installed): View the statistics for a specific network protocol: Trace the routes without looking up names: System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/amework/Versions/A/Resources/airport -s System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/amework/Versions/A/Resources/airport -I Get information about the airport connection on your system: Ping the hostname 5 times and then stop the ping:Ĭustomize the source IP during your ping: Launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ Launchctl unload -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ Socketfilterfw -t “/Applications/FileMaker Pro/FileMaker Pro.app/Contents/MacOS/FileMaker Pro”Īdd a route so that traffic for 10.0.0.0/32 communicates over the 10.0.9.2 network interface: Launchctl load /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/.plist launchctl load /System/Library/LaunchAgents/.plistĪllow an app to communicate outside the system through the application layer firewall: Launchctl unload /System/Library/LaunchAgents/.plist launchctl unload /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/.plist Obtain the dns servers used on the Wi-Fi interface: Networksetup -setmanual Wi-Fi 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1Ĭonfigure the dns servers for a given network interface: Ipconfig set en1 BOOTP & ipconfig set en1 DHCPĮcho "add State:/Network/Interface/en0/RefreshConfiguration temporary" | sudo scutil Set the interface called Wi-Fi to obtain it if it isn’t already Networksetup -ordernetworkservices “Wi-Fi” “USB Ethernet” Networksetup -setnetworkserviceenabled offĬhange the order of your network services: Networksetup -renamenetworkservice Ethernet Wired
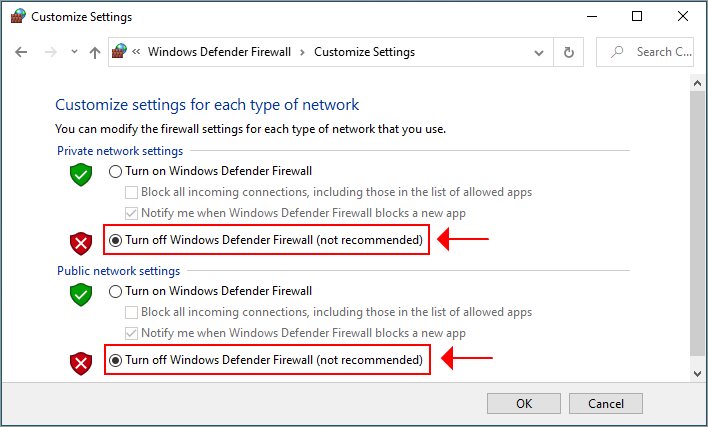
Rename the network service called Ethernet to the word Wired: List all of the network interfaces on the system: Switch the active location to a location called Work, but also show the GUID of that location so we can make scripties with it laters: Switch the active location to a location called Work: Networksetup -createlocation Work populate Obtain the active location the system is using:Ĭreate a network location called Work and populate it with information from the active network connection: Show a list of locations on the computer: Get information about how en0 got its dhcp on: Ipconfig getoption en0 domain_name_server Same thing, but setting and echoing a variable: After writing up the presentation for MacSysAdmin in Sweden, I decided to go ahead and throw these into a quick cheat sheet for anyone who’d like to have them all in one place.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
